Ambient particulate matter (PM) can penetrate deeply into the respiratory system, which has been linked to the increasing incidence and mortality of lung cancer. The International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) has classifed PM in outdoor air as a Group I carcinogen and confirmed that exposure to PM increased the risk of lung cancer, but the principal toxic components and molecular mechanism remain to be further elucidated.
To solve the above issues, researchers from the Center for Excellence in Regional Atmospheric Environment at Institute of Urban Environment, Chinese academy of sciences, collaborating with Laboratory for Earth Surface Processes at College of Urban and Environmental Sciences, Peking University, treated human lung adenocarcinoma A549 cells with water-extracted PM10 (WE-PM10) collected from Beijing, China. The molecular mechanism of lung cancer cell metastasis induced by WE-PM10 was studied.
The results showed that exposure to 25 and 50 μg/ml of WE-PM10 for 48 h significantly suppressed miR-26a to upregulate lin-28 homolog B (LIN28B), and in turn activated interleukin 6 (IL6) and signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) in A549 cells, subsequently contributing to enhanced epithelial–mesenchymal transition (EMT) and accelerated migration and invasion. In vivo pulmonary colonization assay further indicated that WE-PM10 enhanced the metastatic ability of A549 cells. In addition, luciferase reporter assay demonstrated that 3′untranslated region of LIN28B was a direct target of miR-26a.
Last but not the least, the key toxic contribution of metals in WE-PM10 was confirmed by the finding that removal of metals through chelation significantly rescued WE-PM10-mediated in?ammatory, carcinogenic and metastatic responses. This research was published in Archives of Toxicology with the title of "MiR-26a functions as a tumor suppressor in ambient particulate matter-bound metal-triggered lung cancer cell metastasis by targeting LIN28B-IL6-STAT3 axis". This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the Youth Innovation Promotion Association, CAS, and the Knowledge Innovation Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, etc.
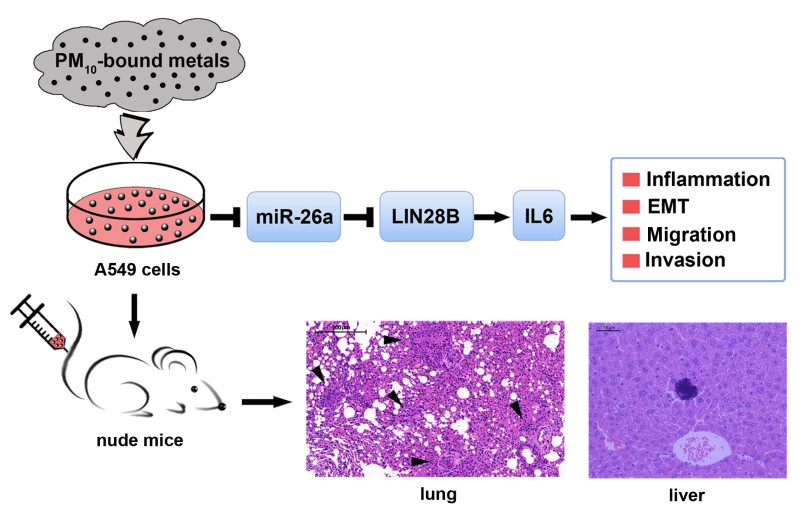
Figure The molecular mechanism of PM10-bound metals-triggered lung cancer cell metastasis