New forms of international cooperation and technology competition with China are the main drivers of public investment in energy innovation, though it remains insufficient to help meet climate goals.
As the ongoing Russo-Ukrainian War to strain global energy supplies, some European countries have begun to cut back on their use of oil and natural gas. Other countries, however, have sought to boost domestic production of fossil fuels to drop prices and ease their current fuel crunch.
That strategy runs in conflict with the emissions reductions needed to meet the 2-degree Celsius climate goal outlined in the Paris Agreement. Achieving climate goals requires a fundamental transformation in the way we supply and use energy, a challenge that can only be achieved through energy innovation.
New analysis led by researchers at the Chinese Academy of Sciences, University of California, Berkeley, the University of Cambridge, and Harvard University, offers insight into the trajectory of energy research, development and demonstration (RD&D) that may help policymakers recalibrate their strategy to drive innovation. Published September 12 in the journal Nature Energy, the findings show that participating in Mission Innovation, a new form of international cooperation, and intensifying technology competition from China are the strongest drivers of funding for clean energy RD&D.
“China remains the second largest contributor and has played an important role in promoting global energy RD&D,” said Tong Xu, an assistant professor at the Institute of Urban Environment, Chinese Academy of Sciences, and a Fellow at the Cambridge Centre of Environment, Energy and Natural Resource Governance (C-EENRG), University of Cambridge.
“By contrast, we do not find that stimulus spending after the financial crisis was associated with a boost in clean energy funding,” said Jonas Meckling, a UC Berkeley professor in the Department of Environmental Science, Policy, and Management and first author of the study.
Monitoring growth and change
Tracking the evolution and variation in “new clean” technologies—a category that includes renewables like solar and wind, hydrogen fuel cells, and improvements in energy efficiency and storage—is central to understanding if energy innovation funding is on track to help achieve emissions reductions needed to achieve the Paris climate goals.
Estimates from the International Energy Agency (IEA) indicate that 35 percent of global emissions reductions rely on prototype technology or innovations that haven’t been fully deployed. Reaching net zero within the global economy will require long-term financial commitments by governments to develop substitutes for fossil fuels.
To conduct their analysis, Dr. Tong Xu and co-authors created two datasets: one tracked RD&D funding from China, India and IEA member countries; the other inventoried 57 public energy innovation institutions relating to decarbonization across eight major economies. They found that energy funding among seven of the eight major economies grew from $10.9 billion to $20.1 billion between 2001 and 2018, an 84-percent increase. “But even though new clean energy funding has grown significantly, it has diverted RD&D funding from nuclear technologies and not from fossil fuel,” said Meckling.
Within that time period, the analysis found, funding for nuclear energy RD&D fell from 42 percent of all money spent to 24 percent. Fossil fuels remain deeply ingrained in public energy RD&D. That level of investment in clean energy innovation remains insufficient to achieve a meaningful level of global emissions reduction, according to University of Cambridge professor of climate change policy Laura Diaz Anadon.
“Annual funding for public energy RD&D would have needed to have at least doubled between 2010 and 2020 to enable future energy emissions cuts approximately consistent with the 2-degree Celsius goal,” she said.
But even with the growing public investment in clean energy technologies, the authors found that the public institutions tasked with funding, coordinating and performing RD&D are not transforming at a pace fast enough to facilitate rapid decarbonization. They are also not focusing enough on commercializing clean energy technologies.
“While we have seen the creation of a lot of new energy innovation agencies since 2000, they experimented only marginally with designs that bridge lab to market and manage only a fraction of total energy RD&D funding,” said co-author Esther Shears, a PhD candidate in UC Berkeley’s Energy and Resources Group.
Explaining shifts in RD&D
The researchers were initially uncertain about what drives the expansion of public energy RD&D funding and transformation of institutions. Past analysis has focused on energy prices.
“Oil prices can be a driver for governments to spend more on energy innovation because you want to look at alternative technologies if it's costly to use oil,” said Clara Galeazzi, co-author and postdoctoral fellow at Harvard University, who pointed to alternative energy investments following global price shocks of the 1970s and 2000s. “But clean energy RD&D continued to grow even after oil prices declined, which required us to think about other drivers.”
In tracking the last two decades of energy funding among major economies, the authors holistically evaluated how the “3 Cs”—financial crisis, international cooperation through Mission Innovation, and technology competition from China—transformed public energy funding and institutions.
“We show that Mission Innovation is associated with major economies scaling their clean energy RD&D funding,” said Shears. “Technological competition with China also matters, as it creates an incentive to invest in future growth sectors where China has taken a lead—including various clean energy technologies.”
Stimulus spending after economic crises like the Great Recession (2007-09) did little to boost clean energy efforts. Instead, the authors found that economic recovery funds typically boosted RD&D funding for fossil fuels and nuclear technology. Stimulus spending during the recession during the global COVID-19 pandemic also reflects this pattern.
Though international cooperation and competition have been effective at driving changes to clean energy RD&D in the past, the authors caution against taking the successful interplay of RD&D cooperation and technology competition for granted going forward.
“We live in times of heightened geopolitical tensions—China recently announced plans to stop climate cooperation with the US,” said Meckling, adding that maintaining the balance of RD&D cooperation and technology competition requires supportive policies. “Government officials need to focus on embedding energy innovation in effective industrial policy strategies to be able to turn innovation into competitive advantages.”
“They also need to strengthen global trade cooperation to facilitate fair and open competition in clean energy technology markets that continue to incentivize governments to invest in clean energy RD&D,” Meckling said.
Co-authors on the study include Meckling; Energy and Resources Group PhD candidate Esther Shears; University of Cambridge professor of climate change policy Laura Diaz Anadon and Institute of Urban Environment, Chinese Academy of Sciences assistant professor, Cambridge Centre of Environment, Energy and Natural Resource Governance fellow Tong Xu; and Harvard University postdoctoral fellow Clara Galeazzi.
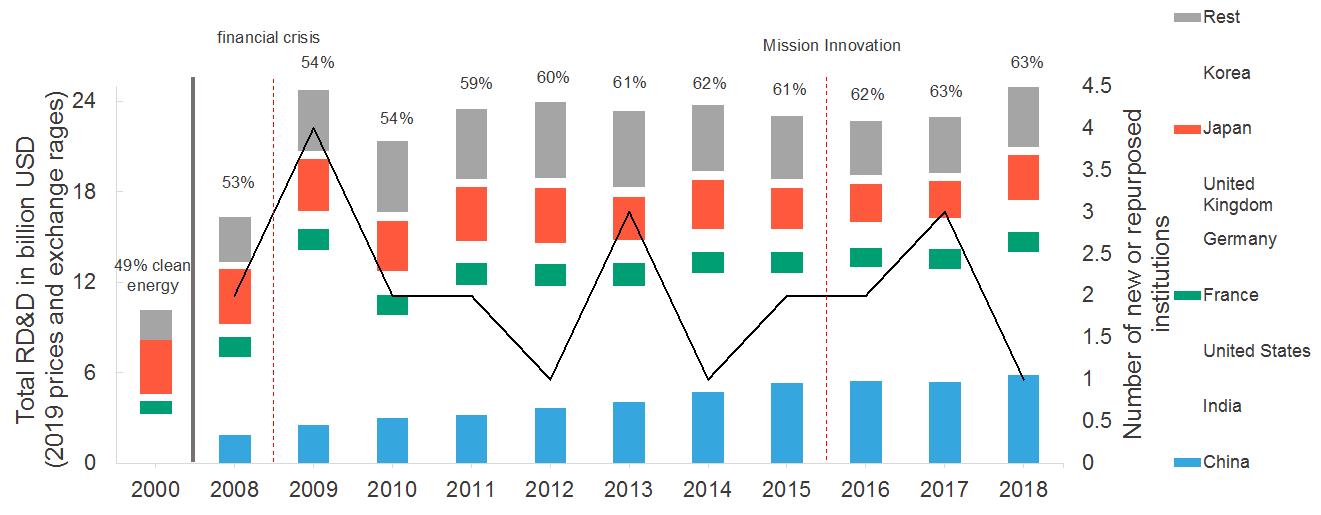
Fig. 1 Evolution of RD&D funding by country and of innovation institutions. Total energy RD&D funding by country (columns, left axis), new or repurposed institutions (solid black line, right axis), percentage of total RD&D funding allocated to new clean (text above columns); financial crisis and Mission Innovation (vertical red dashed lines). The 2000 bar and clean percentages do not include China or India and the 2008 and 2009 bars and percentages do not include India. The total known energy RD&D funding for the M8+rest of IEA in 2018 was 24.9 billion USD (2019 prices and exchange rates).